This comprehensive guide sets the standard for selecting the correct connector and power solution for modern life in the United States.
It explains the four non-negotiables readers must check before any purchase: voltage identity, adequate amperage headroom, correct polarity, and a precise physical connector fit.
The goal is to make selection simple and reliable so they can protect gear and avoid costly mistakes.
The structure first covers fundamentals, then a step-by-step checklist to confirm a device’s label specs and connector details. It also points to device-specific sections for dash cams, phones, tablets, and many car brands.
Readers will gain practical rules to pick the right adapter on the first try, know when a plug converter is needed for travel, and understand exceptions like non-USB radar detectors and certain 12V cameras.
Key Takeaways
- Verify voltage first; mismatch risks damage.
- Allow extra amperage for safe operation.
- Confirm polarity and physical connector fit.
- Use internal links to jump to device-specific guidance.
- Distinguish plug adapters from voltage converters for travel.
Adapter Compatibility Fundamentals
Start with four technical checks that decide whether a power supply will safely run a device.
Voltage Matching: Why Identical Voltage Protects Devices
Match the output voltage exactly to the device input. Close voltages may power a unit briefly, but identical voltage is the reliable safety standard.
Using higher or lower volts risks malfunction, shortened lifespan, or immediate damage even if the device appears to work.
Amperage Headroom: Equal Or Greater Amps For Safe Power
The power source must supply equal or greater current than the device needs. Devices draw only what they require.
An undersized unit can run hot, throttle, or shut down under load.
Polarity Checks: Reading The Inner/Outer Plug Diagram
Confirm the polarity diagram on the device label and match it exactly. Reversing center-positive versus center-negative can short internal circuits.
Connector And Plug Shape: Ensuring A Physical Fit
Verify barrel diameter, length, keying, or USB type so the plug seats fully. A loose fit causes arcing, intermittent power, or damage to contacts.
| Criterion | What To Check | Risk If Mismatched | Quick Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Exact output vs. device input (V) | Damage, erratic behavior | Compare numbers line‑by‑line on labels |
| Amperage | Adapter ≥ device current (A) | Overheat, shutdown, reduced life | Choose equal or higher amp rating |
| Polarity | Inner/outer +/− diagram | Instant short, blown components | Match symbols exactly; use a multimeter if unsure |
| Connector | Barrel size or USB type | Intermittent power, arcing | Use the exact mating plug or keyed tip |
USB-C Power Delivery note: ensure the adapter’s negotiated profiles match the device and use a compliant cable for correct delivery.
When all four criteria align, the pairing is generally safe and reliable.
How To Choose The Right Adapter Step By Step
A concise, ordered process removes guesswork when selecting the correct power source for any device. The steps below turn technical checks into a quick, repeatable routine.

Identify Device Power Specs On The Label Or Manual
Step 1 — Find the Specs: Read the label or manual and note voltage (V), current (A or mA), the polarity symbol, and whether the output is AC or DC.
Verify Connector Type Before You Buy
- Step 2 — Match Voltage Exactly: Choose an adapter with identical output voltage and the same AC/DC type. Never assume “close enough.”
- Step 3 — Ensure Amperage Headroom: Pick one rated for equal or higher amperage so it runs cooler and more reliably.
- Step 4 — Confirm Polarity: Match the center‑positive or center‑negative diagram. If a universal model has a switch, set it before powering on.
- Step 5 — Identify Connector Type: Note barrel dimensions, USB type, or proprietary plugs; measure if unknown to avoid loose fits.
- Step 6 — Consider USB‑C PD Profiles: For USB‑C, ensure the adapter and cable support the voltage profiles your device expects.
- Step 7 — Test Smartly: Power up while watching for heat or instability; use a meter if available.
| Check | Action | Why It Matters | Quick Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Match number and AC/DC | Prevents damage and malfunctions | Compare labels side‑by‑side |
| Amperage | Choose equal or higher | Ensures stable operation | Extra amps run cooler |
| Connector | Confirm size and fit | Prevents arcing and dropouts | Measure if unspecified |
For detailed buying guidance, see how to choose power adapter. Label and store each supply to avoid future mix‑ups and protect equipment.
Adapter Compatibility Guide: Device-Specific Links And Exceptions
This section maps brand mirror ports and power exceptions so readers match the right plug and power source quickly.

Dash Cams & USB Devices: Most USB‑powered devices work with standard 5V supplies. Exceptions include radar detectors that need 12V over RJ11 (Escort, Uniden, Valentine) and cameras that require 12V barrel jacks (Thinkware, BlackVue).
Vehicle Mirror Ports By Brand
The table below summarizes common mirror connectors by make and typical model notes.
| Brand | Common Pin Types | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Toyota / Lexus | 10‑pin Type B, 12‑pin Type A, 14‑pin, 7‑pin | Do not plug into Safety Sense computer; use autodimming mirror connector only. |
| Ford | 5‑pin Type F, 3‑pin Type B, 16‑pin Type A | Frameless vs framed mirrors determine pin style; check model/year. |
| Honda / Acura | 7‑pin Type A, 12‑pin B/A, 8‑pin | Trim changes can swap pins; recent models may use 8‑pin. |
| Nissan / Infiniti | 10‑pin Type A, 7‑pin Type B, 12‑pin Type A | Some Infiniti trims share Toyota/Tacoma connector. |
Important Exceptions & Model‑Year Nuances
Older Garmin dash cams (20, 45, 55, 65) require proprietary charger modules despite having USB plugs; newer Garmin units accept standard USB power.
Visual inspection is crucial: trim level, dealer vs. factory mirror, and optional packages often change the connector. For brand history and evolution of plugs, see the detailed guide on adapters through the ages.
Travel Power And Plug Types For The United States And Beyond
Travelers must know which flat‑blade sockets accept U.S. plugs before they pack charging gear.
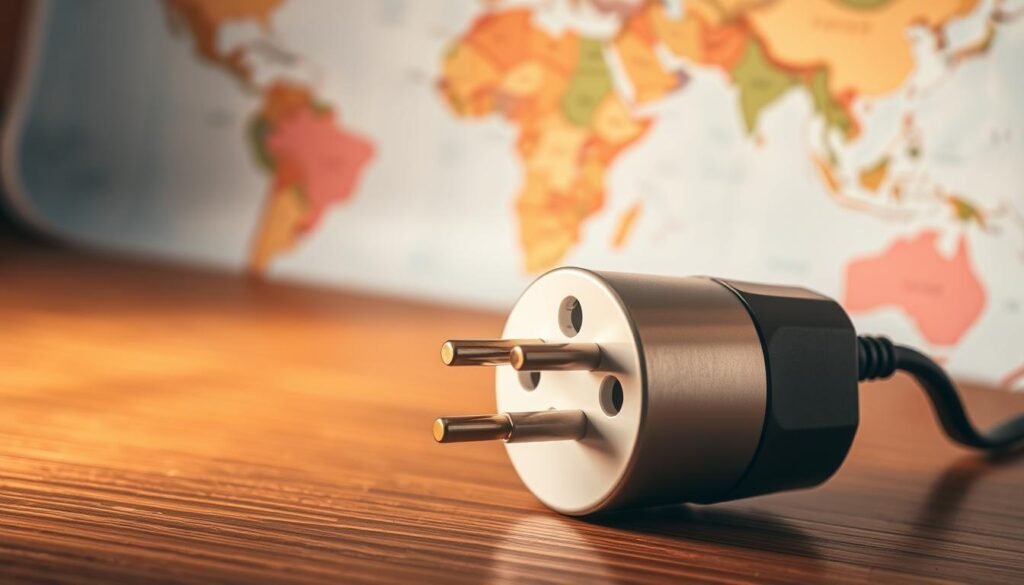

U.S. Standard: The United States uses Type A (two flat blades) and Type B (two flat blades plus ground). Most North American plugs fit these sockets directly.
Matching Country Plug Types To Your Adapter
Many countries and territories accept U.S.‑style flat blades. This list includes Canada, Mexico, Japan, Taiwan, Hong Kong, the Philippines, Thailand, Vietnam, parts of the Caribbean, and much of Latin America. Mainland China can vary; some outlets lack blade holes and blades may be slightly shorter.
- Voltage Awareness: Japan commonly uses 100V; the U.S. uses 120V. Other countries may supply 220–240V. Verify the input range on your power brick (for example, “Input: 100–240V 50/60Hz”).
- Adapter vs. Converter: If the device accepts 100–240V, a plug adapter is enough. If it is 120V‑only, carry a step‑down converter.
- Grounding & Safety: When a destination accepts only two flat blades, ensure grounded plugs remain safe or use an approved solution that preserves protection.
Packing tip: Bring a multi‑port USB charger that supports 100–240V and a solid U.S.‑to‑international plug solution. For practical travel steps see this international travel guide and a concise types of electrical adapters.
Conclusion
Practical rules make choosing the right supply predictable and safe for every device.
Match voltage exactly, allow equal or greater amperage, confirm polarity, and use the correct connector for a secure fit. These steps prevent damage and reduce returns.
Verify labels and mirror plug types before ordering. For dash cams and in‑vehicle gear, consult brand guides and the exceptions list to avoid RJ11 and 12V barrel‑jack pitfalls.
Travelers should use a universal, 100–240V charger with the right plug tip when the device supports the destination voltage. A quick visual check of the connector shroud often prevents first‑try failures.
For a concise buying checklist and practical tips, see how to choose the right power adapter.